ranger - Random Forest
rangerVivid.RmdThis guide is designed as a quick-stop reference of how to use some
of the more popular machine learning R packages with vivid.
In the following examples, we use the air quality data for regression
and the iris data for classification.
ranger - Random Forest
The ranger package in R is a fast implementation of
Random Forests, leveraging optimized C++ code for efficiency.
Regression
# load data
aq <- na.omit(airquality)
# build rf model
rf <- ranger(Ozone ~ ., data = aq)
# vivid
vi <- vivi(data = aq, fit = rf, response = 'Ozone')Heatmap
viviHeatmap(mat = vi)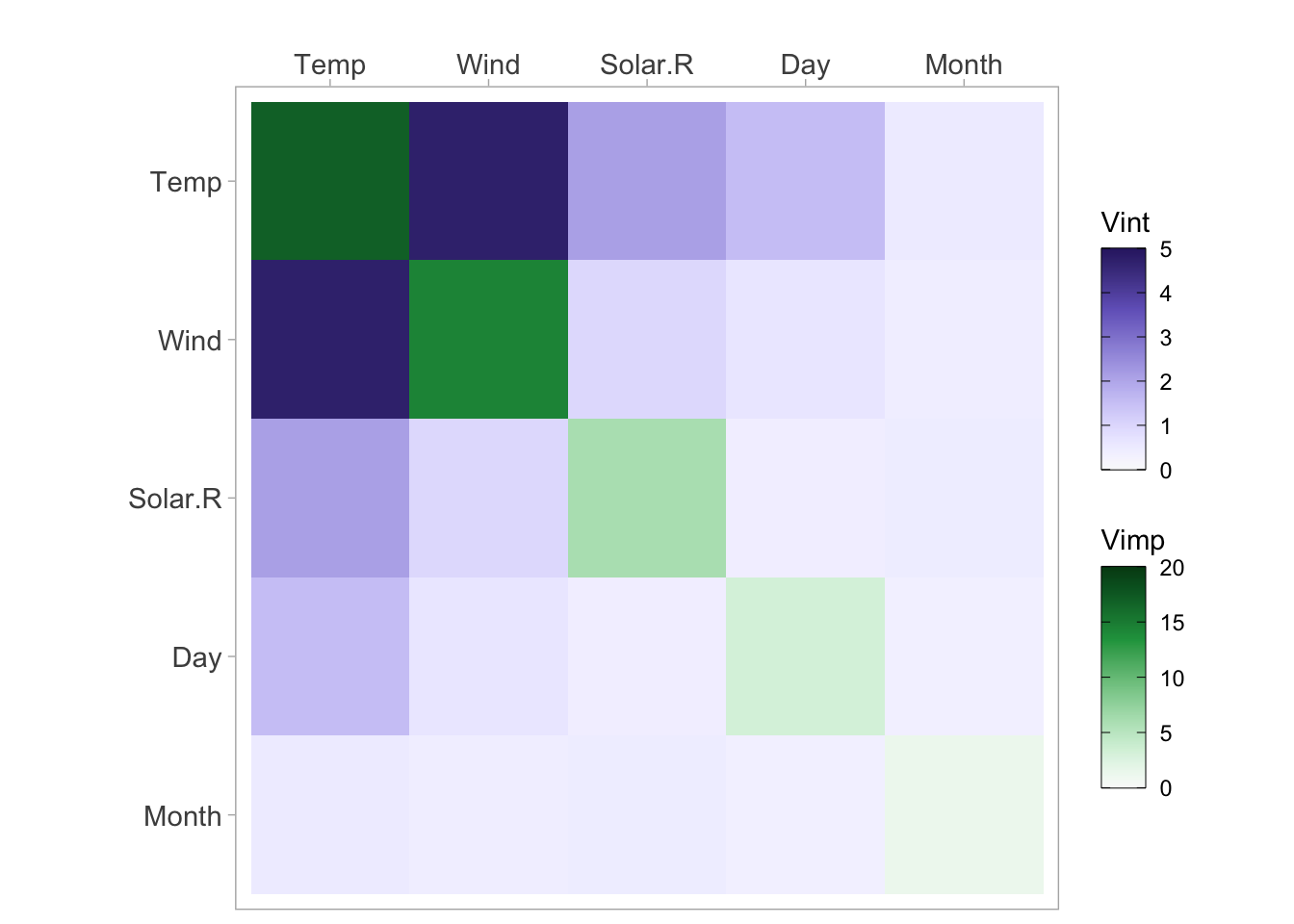
PDP
pdpPairs(data = aq,
fit = rf,
response = "Ozone",
nmax = 500,
gridSize = 20,
nIce = 100)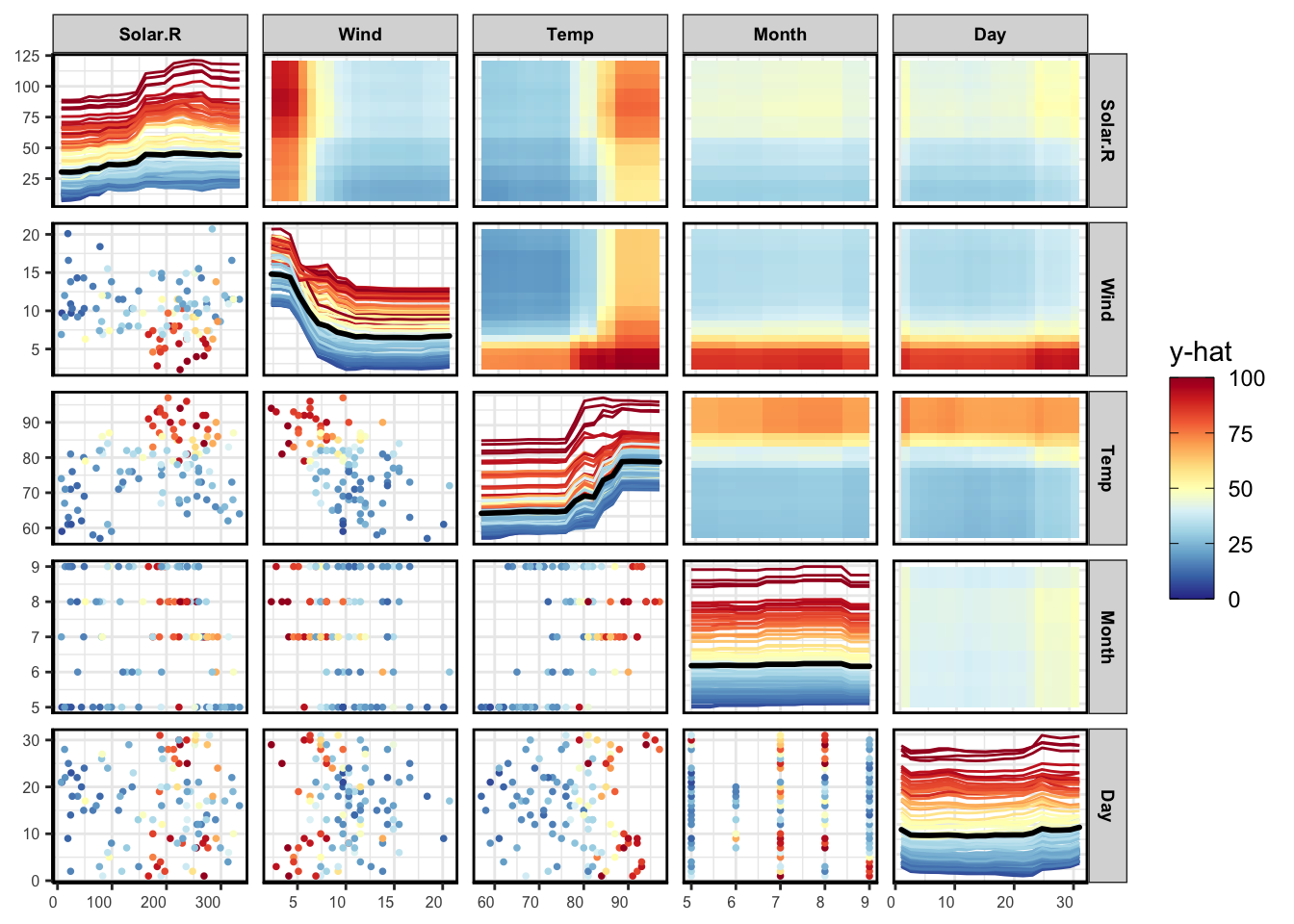
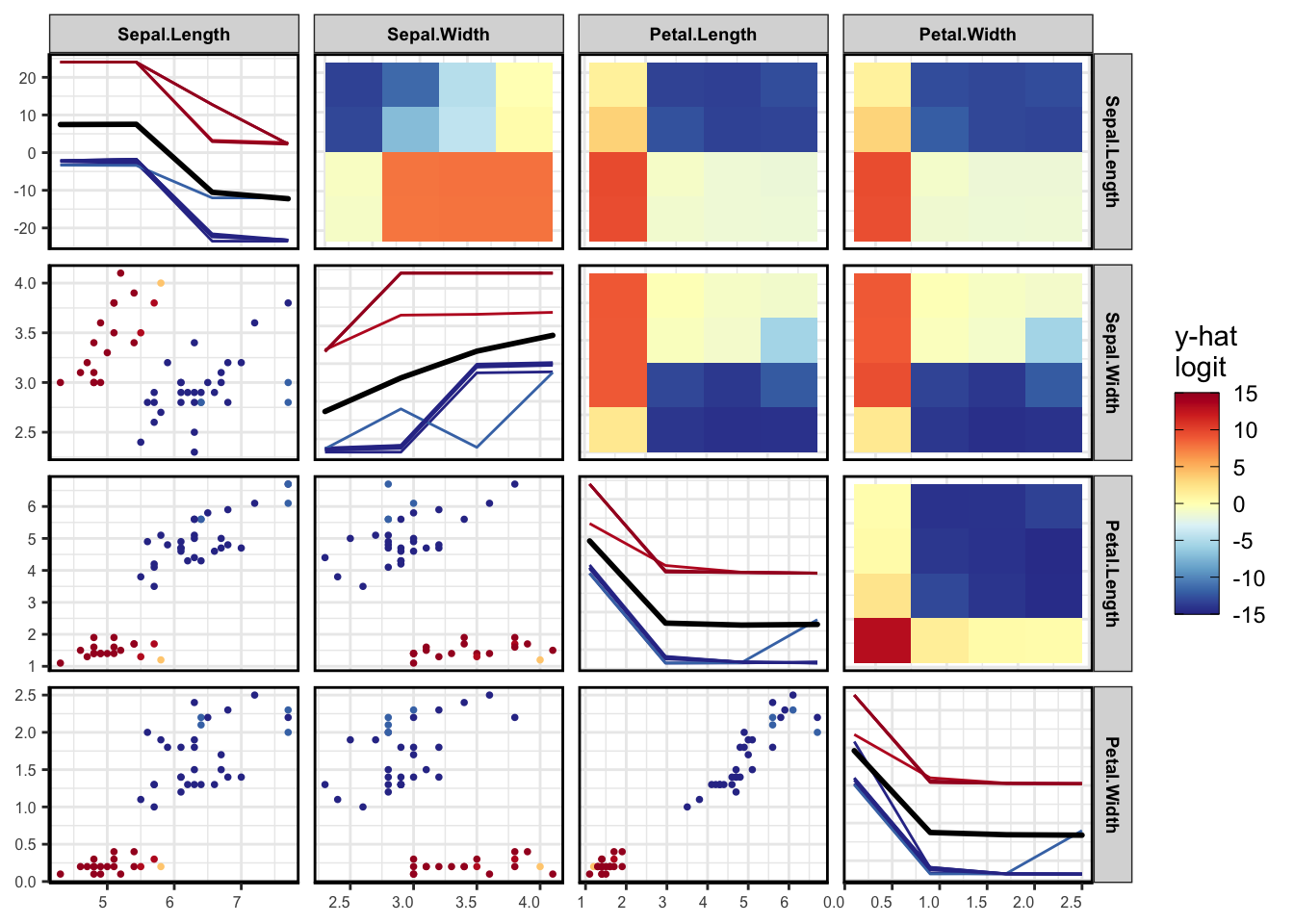
Classification
# Load the iris dataset
data(iris)
# Train
rf <- ranger(Species ~ ., data = iris, probability = T)
vi <- vivi(data = iris, fit = rf, response = 'Species', class = 'setosa')Heatmap
viviHeatmap(mat = vi)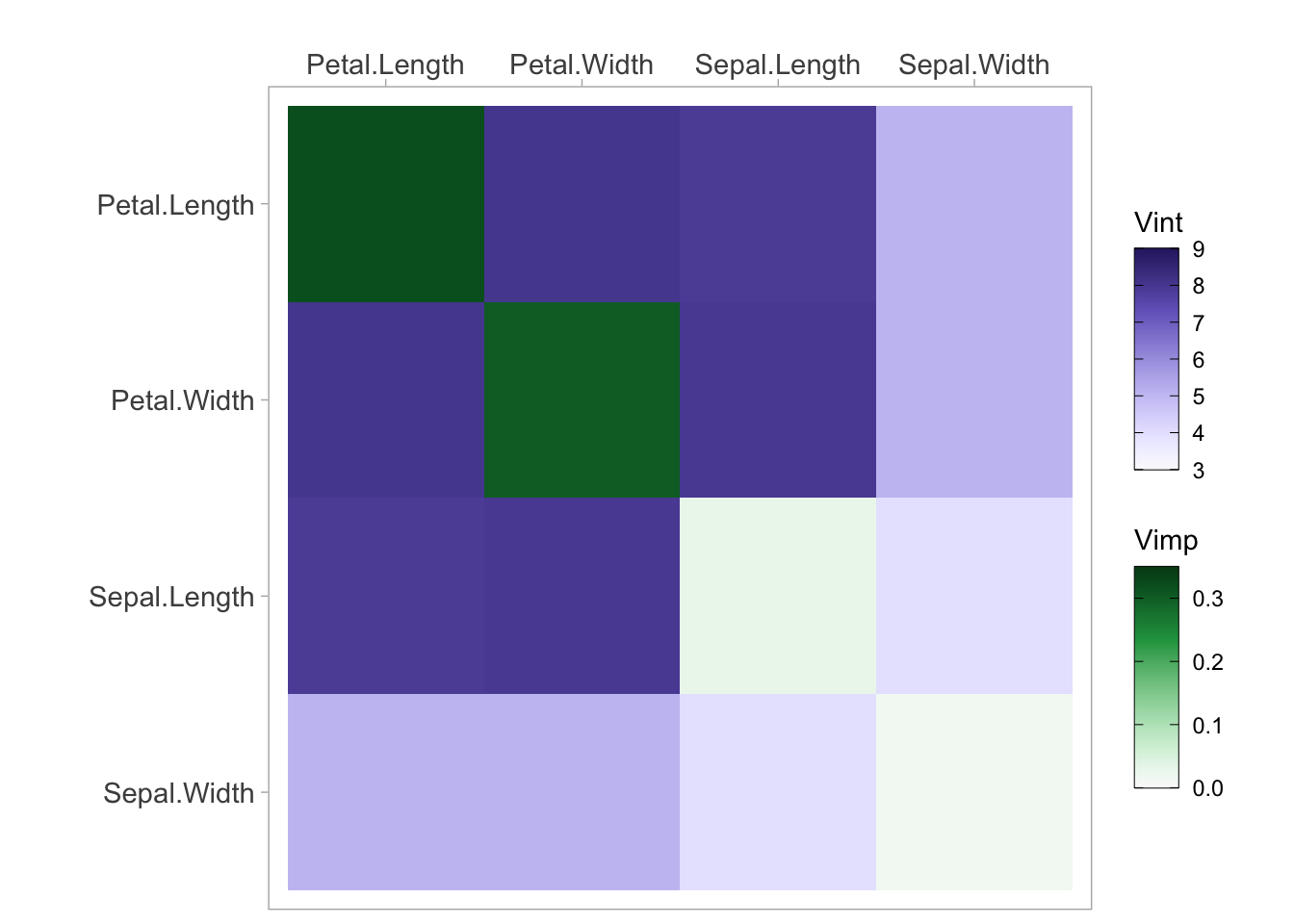
PDP
pdpPairs(data = iris,
fit = rf,
response = "Species",
nmax = 50,
gridSize = 4,
nIce = 10,
class = 'setosa')