caret - Neural Network
caretVivid.RmdThis guide is designed as a quick-stop reference of how to use some
of the more popular machine learning R packages with vivid.
In the following examples, we use the air quality data for regression
and the iris data for classification.
caret - Neural Network
The caret package (short for Classification And
REgression Training) in R provides a unified interface to streamline the
process of creating predictive models. In the following example, we use
the caret package to utilize a neural network model fit via
the nnet package. As caret is catered for in
vivid, there is no need for a custom predict function
here.
Regression
# load data
aq <- na.omit(airquality)
# build caret nnet model
nn <- train(Ozone ~ ., data = aq, method = "nnet", trace = FALSE, linout = TRUE, maxit = 200)
# vivid
vi <- vivi(data = aq, fit = nn, response = 'Ozone')Heatmap
viviHeatmap(mat = vi)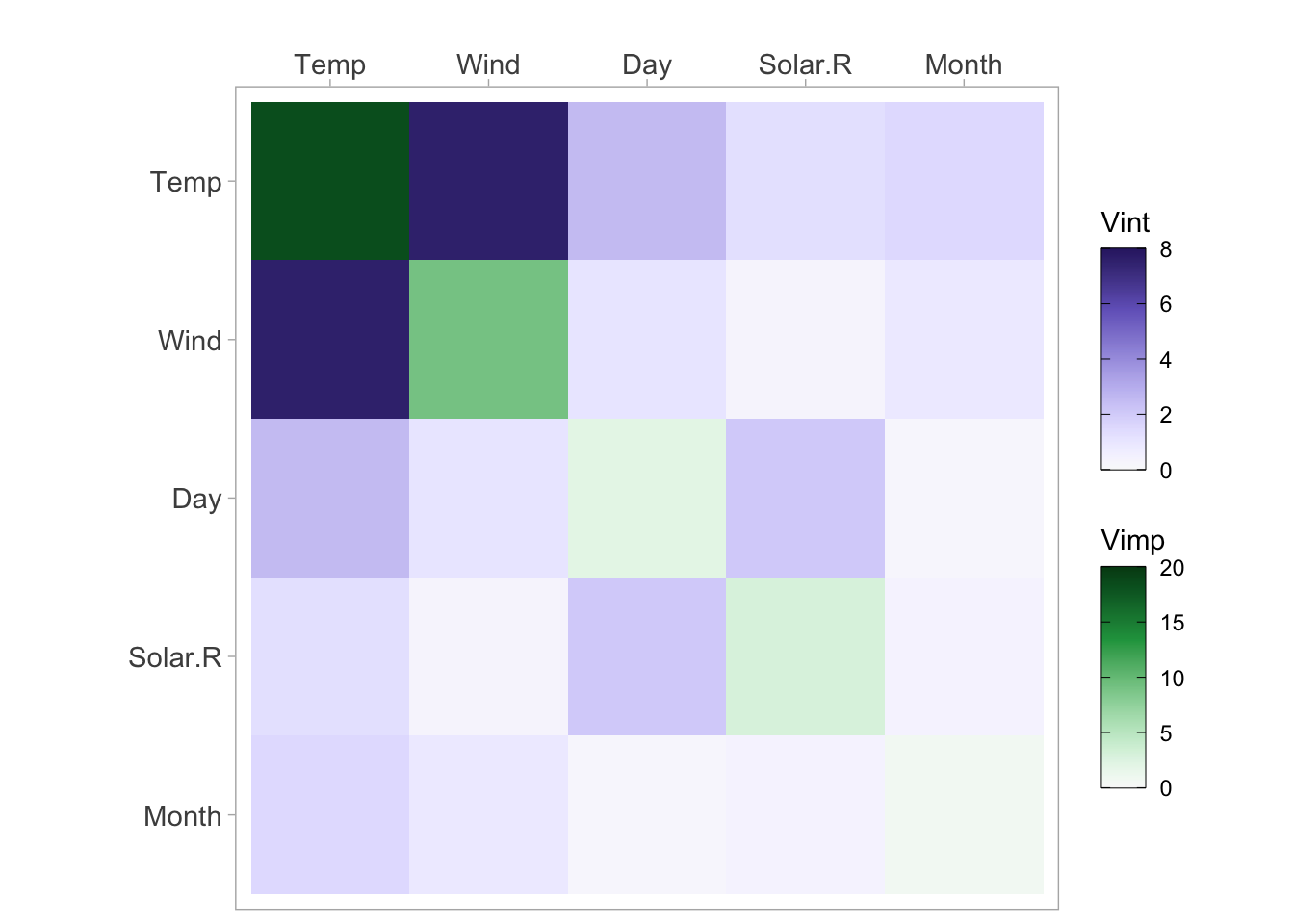
PDP
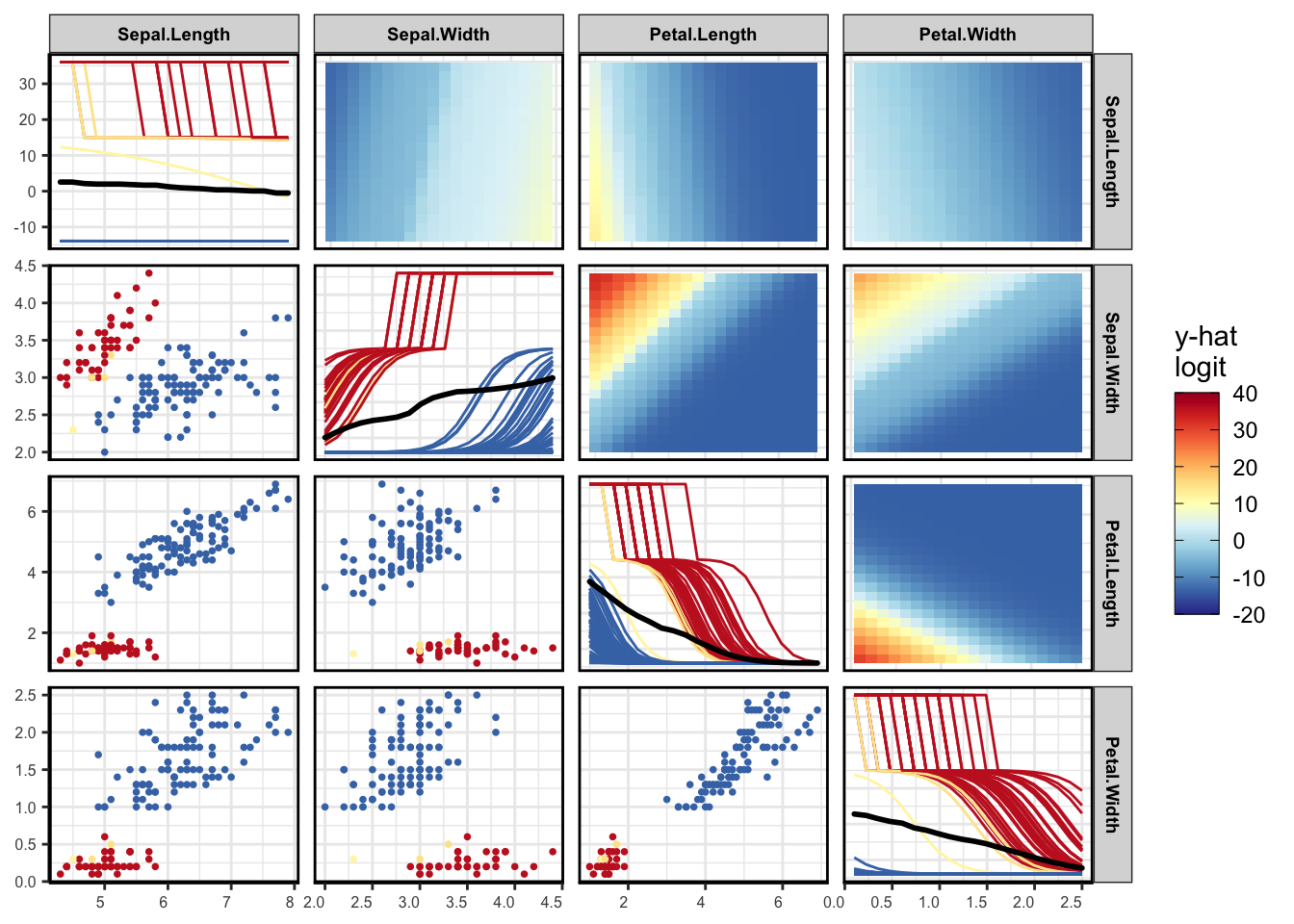
pdpPairs(data = aq,
fit = nn,
response = "Ozone",
nmax = 50,
gridSize = 4,
nIce = 10)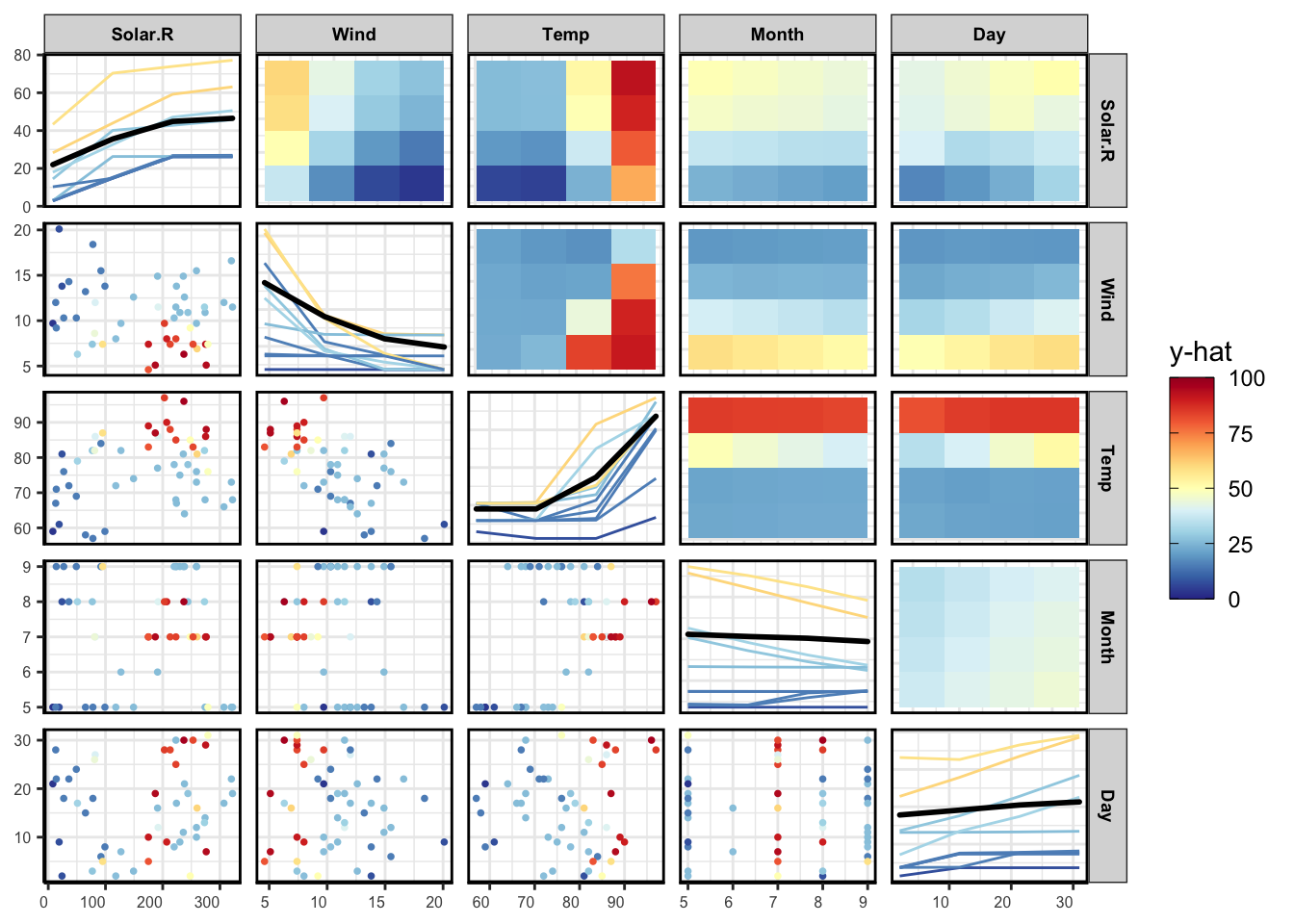
Classification
# Load the necessary library
library("caret")
# Load the iris dataset
data(iris)
irisMod <- iris
# Convert the Species to a binary classification: Setosa or not Setosa
irisMod$Species <- as.factor(ifelse(irisMod$Species == "setosa", "setosa", "not_setosa"))
# Train a neural network model
nn <- train(Species ~ ., data = irisMod, method = "nnet",
trControl = trainControl(method = "cv", number = 5),
tuneLength = 1,
linout = FALSE, # this is set to FALSE for classification problems
trace = FALSE,
maxit = 200)
vi <- vivi(data = irisMod, fit = nn, response = 'Species')Heatmap
viviHeatmap(mat = vi)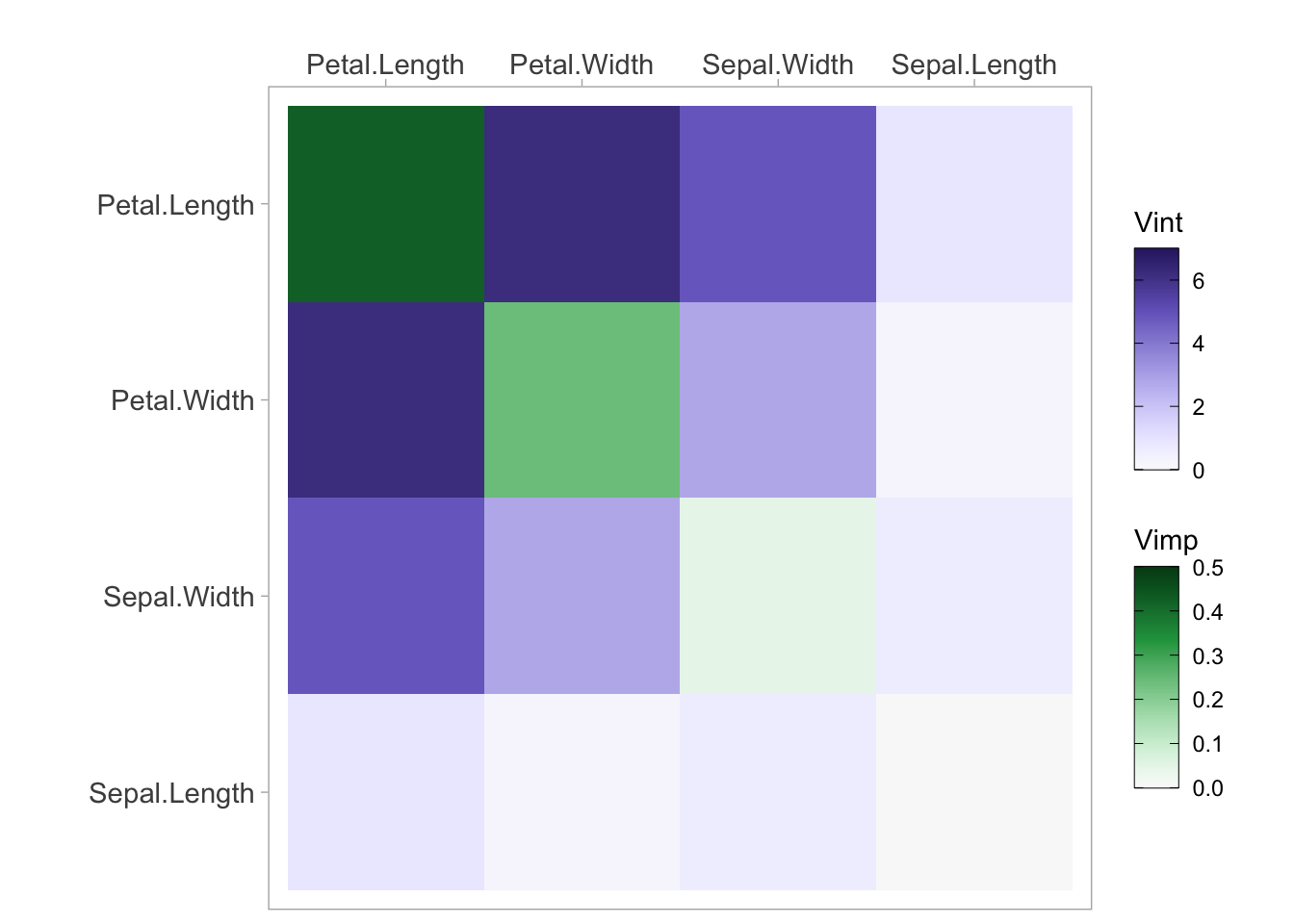
PDP
pdpPairs(data = irisMod,
fit = nn,
response = "Species",
nmax = 500,
gridSize = 20,
nIce = 100,
class = 'setosa')